Why On-Page SEO Mistakes Cost You Traffic
On-page SEO mistakes prevent your content from ranking despite your best efforts. Small errors compound over time, hiding your pages from search engines and driving potential visitors to competitors instead.
Understanding common optimization mistakes helps you avoid them before they damage rankings. Even websites with great content lose organic traffic when technical errors, poor optimization, or outdated tactics sabotage their SEO performance.
The Hidden Cost of SEO Errors
Most website owners do not realize optimization mistakes are hurting them until traffic drops significantly or they run a comprehensive audit. By then, competitors have captured rankings and audience attention.
SEO errors waste your content creation efforts, reduce return on investment from marketing, hurt user experience and conversions, and make recovery harder the longer they persist.
Critical Title Tag and Meta Description Mistakes
Title tags and meta descriptions are your first impression in search results. Mistakes in these elements reduce click-through rates even when you rank well, effectively wasting good rankings.
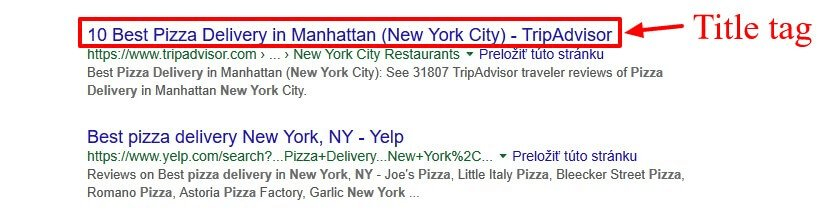
Many websites either neglect these elements entirely or optimize them incorrectly, missing opportunities to attract clicks from searchers actively looking for their content.
Missing or Duplicate Title Tags
Every page needs a unique title tag describing what it contains, yet many sites have missing titles, duplicate titles across multiple pages, or default titles like “Home” or “Untitled” that provide no information to searchers.
Title Tags That Are Too Long or Too Short
Titles exceeding 60 characters get cut off in search results, hiding important information, while titles under 30 characters waste valuable space and miss keyword opportunities.
Ignoring Meta Descriptions Completely
Pages without meta descriptions let Google create descriptions from page content, often producing poor summaries that do not convince users to click your result over competitors.
Generic or Duplicate Meta Descriptions
Using the same description across multiple pages or writing generic descriptions like “Welcome to our website” wastes opportunities to differentiate pages and attract targeted traffic.
Devastating Keyword Optimization Errors
Keyword mistakes range from over-optimization that triggers spam filters to under-optimization that leaves search engines confused about page topics.
Keyword Stuffing and Over-Optimization
Repeating keywords unnaturally throughout content, forcing keywords into every sentence, using exact keywords excessively in headers, and creating unreadable content for SEO purposes all trigger spam detection and hurt rankings.
Keyword Cannibalization Problems
Multiple pages targeting the same keyword compete against each other, confusing search engines about which page to rank and diluting ranking power across pages instead of consolidating authority.
Targeting Wrong or Irrelevant Keywords
Optimizing for keywords with no search volume, targeting keywords that do not match page content, ignoring search intent behind keywords, and choosing keywords too competitive for your authority level waste optimization efforts.
Neglecting Long-Tail Keywords
Focusing only on broad, competitive keywords while ignoring specific long-tail variations with clear intent and higher conversion rates misses easier ranking opportunities.
Content Quality Mistakes That Tank Rankings
Content quality directly impacts rankings more than any other single factor. Poor content cannot rank well regardless of technical optimization.

Many websites publish content without considering whether it actually helps users, provides unique value, or matches what searchers truly want.
Thin Content With Little Value
Pages with under 300 words rarely provide comprehensive information, shallow content that barely touches on topics, and pages created just to target keywords without offering real value all perform poorly.
Duplicate Content Across Pages
Copying content from other pages on your site, using manufacturer descriptions without modification, creating multiple pages with nearly identical content, and republishing content without adding new value confuse search engines and waste crawl budget.
Ignoring Search Intent
Creating informational content for commercial keywords, writing product pages when users want guides, providing long articles when users need quick answers, and mismatching content format to user expectations hurt rankings despite keyword optimization.
Outdated or Inaccurate Information
Old statistics and data, outdated best practices, broken references, and incorrect information damage trust and reduce rankings as Google prioritizes accuracy and freshness.
Header Tag Structure Failures
Header tags organize content and help search engines understand page hierarchy. Poor header structure makes content hard to scan and reduces SEO effectiveness. Many websites either ignore headers completely or use them incorrectly, missing both user experience and SEO benefits.
Multiple H1 Tags on One Page
Using several H1 tags confuses page hierarchy, makes main topics unclear, and dilutes the SEO value of your primary heading.
Skipping Heading Levels
Jumping from H1 to H3 without H2, using H4 before H3, and creating illogical heading hierarchies break document structure and accessibility standards.
No Headers or Poor Header Usage
Writing long content without any headers, using headers only for styling not structure, making headers too generic, and failing to include keywords in important headers reduce scannability and SEO performance.
Image Optimization Oversights
Images enhance content but create SEO problems when not optimized properly. Image mistakes slow page speed and waste opportunities for image search traffic.
Missing Alt Text on Images
Every meaningful image needs descriptive alt text for accessibility and SEO, yet many sites have no alt text, use generic descriptions like “image,” or leave alt attributes completely empty.
Massive Uncompressed Image Files
Uploading images straight from cameras, using unnecessarily high resolutions, choosing wrong file formats, and ignoring compression create slow loading times that hurt both user experience and Core Web Vitals scores.
Generic Image File Names
Image names like IMG_1234.jpg provide no context to search engines, while descriptive file names with relevant keywords help image search rankings and overall page relevance.
Not Using Lazy Loading
Loading all images immediately, even those far below the fold, slows initial page load times and hurts performance metrics when lazy loading could defer off-screen images.
Internal Linking Strategy Mistakes
Many websites randomly link or ignore internal linking entirely, missing opportunities to strengthen their site architecture and improve rankings.
Orphan Pages With No Internal Links
Pages with no links pointing to them are hard for search engines to discover, receive no authority from other pages, and often never rank despite having good content.
Too Many or Too Few Internal Links
Overwhelming pages with dozens of links dilutes link equity, while having too few links misses opportunities to guide users and distribute authority.
Poor Anchor Text Choices
Using generic anchor text like “click here,” over-optimizing anchor text with exact keywords repeatedly, and failing to describe linked content reduce internal linking effectiveness.
Not Updating Old Posts With Links to New Content
Publishing new content without linking from related existing posts, letting old popular posts go stale without fresh links, and missing cross-linking opportunities reduce overall site authority.
URL Structure and Technical Mistakes
Clean URL structure helps both users and search engines understand your site. URL mistakes create confusion and technical problems. Poor URL choices often stem from platform defaults or lack of planning, but they significantly impact crawlability and user experience.
Messy, Non-Descriptive URLs
URLs with random numbers and characters, session IDs in URLs, unnecessary parameters, and cryptic structures reduce click-through rates and make content harder to understand.
Changing URLs Without Proper Redirects
Moving content to new URLs, redesigning sites without redirect plans, deleting old URLs, and creating 404 errors from URL changes lose accumulated authority and confuse search engines.
Using Uppercase Letters or Special Characters
URLs with inconsistent capitalization, underscores instead of hyphens, and special characters create duplicate content issues and accessibility problems.
Mobile Optimization Failures
Mobile-first indexing means Google primarily uses mobile versions of pages for ranking. Mobile mistakes directly hurt all rankings, not just mobile search. Many websites still treat mobile as an afterthought despite mobile traffic dominating most industries.
Not Mobile-Friendly or Responsive
Sites requiring horizontal scrolling, text too small to read, buttons too close together, and layouts breaking on mobile devices face ranking penalties and high bounce rates.
Intrusive Interstitials on Mobile
Large popups covering content, signup forms blocking access, ads interfering with navigation, and interstitials appearing immediately hurt mobile user experience and violate Google guidelines.
Slow Mobile Page Speed
Heavy mobile pages, unoptimized images for mobile, excessive JavaScript, and ignoring mobile network speeds create poor experiences that tank mobile rankings.
Page Speed and Core Web Vitals Issues
Page speed affects both user experience and rankings. Core Web Vitals provide specific metrics Google uses to evaluate page experience. Speed problems compound as sites add features, images, and scripts without considering performance impact.
Ignoring Core Web Vitals Metrics
Not monitoring Largest Contentful Paint, failing to optimize First Input Delay or Interaction to Next Paint, and ignoring Cumulative Layout Shift hurt rankings and user satisfaction.
Render-Blocking Resources
CSS and JavaScript blocking page rendering, no resource prioritization, unoptimized critical rendering path, and loading unnecessary resources slow initial page display.
No Image Compression or Optimization
Serving oversized images, using wrong formats, not implementing lazy loading, and ignoring modern formats like WebP create unnecessarily slow loading.
Schema Markup and Structured Data Errors
Schema markup helps search engines understand content and can trigger rich results. Most websites either ignore schema completely or implement it incorrectly.
No Schema Markup Implementation
Missing out on rich snippets, not helping search engines understand content, ignoring opportunities for enhanced listings, and leaving schema benefits to competitors reduce visibility.
Incorrect Schema Implementation
Using wrong schema types, including invalid markup, missing required properties, and not testing implementation create errors that prevent rich results.
Outdated or Conflicting Schema
Multiple conflicting schema types, using deprecated schema, and not updating schema when content changes confuse search engines and prevent rich result eligibility.
External Linking Mistakes That Damage Credibility
External links to other websites affect your credibility and trustworthiness signals. Linking to low-quality sites or making linking mistakes hurts both user experience and SEO performance.
Many websites either avoid external links completely or link carelessly without considering the quality and relevance of destination sites.
Common External Linking Errors to Avoid
Prevent these external linking mistakes that damage your site’s authority:
- Linking to low-quality or spammy websites
- Never citing authoritative sources for claims
- Broken external links frustrating users
- Misusing nofollow on all external links
- Too many outbound links sending visitors away
- Not opening links in new tabs
- Linking to direct competitors unnecessarily
Canonical Tag and Duplicate Content Problems
Canonical tags tell search engines which version of similar pages to index. Mistakes create duplicate content issues that dilute rankings.
Many websites do not understand when or how to use canonical tags, creating problems instead of solving them.
Missing Canonical Tags
Pages without canonical tags, duplicate content without specified canonical versions, and ambiguous page versions confuse search engines about which page to rank.
Wrong Canonical Implementation
Self-referencing canonicals incorrectly, pointing to wrong pages, creating canonical chains, and contradicting other signals reduce effectiveness.
Fixing Your On-Page SEO Mistakes
Start addressing SEO mistakes systematically by running a comprehensive site audit using tools like Screaming Frog, Semrush, or Ahrefs to identify issues across your entire site. Prioritize fixes based on severity and potential impact by addressing critical technical errors first, fixing high-traffic pages next, and systematically improving lower-priority pages over time.
Create a checklist for new content ensuring future pages avoid common mistakes, implement quality control processes, and establish ongoing monitoring to catch new issues quickly. Remember that SEO is ongoing work requiring regular attention, continuous improvement, staying current with best practices, and adapting to algorithm changes and new ranking factors as they emerge.






