What Are Toxic Backlinks and Why They’re Dangerous
Toxic backlinks are low-quality or spammy links pointing to your website that can harm your search rankings and trigger Google penalties. These harmful links come from suspicious sources like link farms, irrelevant sites, or manipulative link schemes.
Not all backlinks help your SEO. Some actively damage your site’s reputation with search engines, making it crucial to identify and remove toxic links before they cause ranking drops or penalties.
How Toxic Backlinks Harm Your SEO Performance
Google evaluates the quality of sites linking to you as trust signals. When low-quality or spammy sites link to your domain, they can drag down your overall domain authority and trustworthiness.

The impact ranges from subtle ranking decreases to devastating manual penalties that remove your site from search results entirely.
Direct Ranking Impact
Toxic backlinks dilute your link profile quality, association with spam sites reduces domain trust, manipulative link patterns trigger algorithmic devaluation, and Google’s Penguin algorithm specifically targets unnatural links.
Penalty Risks
Manual actions from Google’s review team require reconsideration requests, algorithmic penalties happen automatically without notification, partial penalties affect specific pages or keywords, and complete de-indexing removes sites from search results.
Brand Reputation Damage
Links from adult or gambling sites harm brand perception, association with malware-infected sites creates security concerns, irrelevant link sources confuse your topical authority, and spam directory listings damage professional credibility.
Common Sources of Toxic Backlinks
Understanding where toxic links originate helps you identify and prevent them.
Link Farms and Private Blog Networks
Networks of sites created solely for link building purposes, low-quality content with excessive outbound links, obvious footprints Google easily detects, sites with no real traffic or users, and interconnected link schemes all indicate toxic sources.
Spammy Directories and Listings
Auto-approval directories accepting any submission, general web directories with no editorial standards, foreign language directories unrelated to your business, directories with extremely high outbound link counts, and obvious spam sites masquerading as directories all create toxic links.
Hacked or Compromised Websites
Previously legitimate sites infected with malware, hidden spam links injected into hacked sites, pharmaceutical or adult content spam on compromised domains, and links appearing on penalized websites all represent dangerous link sources.
Negative SEO Attacks
Competitors deliberately building toxic links to your site, sudden unnatural link spikes from suspicious sources, spam comments across low-quality blogs, and mass directory submissions you didn’t authorize all indicate attacks.
Over-Optimized Anchor Text
Excessive exact-match keyword anchors appearing manipulative, unnatural anchor text distribution patterns, commercial keywords used repeatedly, and lack of branded or natural anchor variation all signal problems.
Signs Your Site Has Toxic Backlinks
Certain indicators suggest toxic backlinks may be affecting your site.
Warning Signals to Watch
Sudden unexplained ranking drops, manual action notifications in Search Console, dramatic increases in referring domains overnight, links from completely irrelevant industries, and anchor text over-optimization all warrant immediate investigation.
Google Search Console Alerts
Manual action messages about unnatural links, security issues from linking sites, spam patterns detected by Google, and link-related notifications all require urgent attention.
Traffic and Ranking Changes
Organic traffic declining without clear reason, rankings dropping for money keywords, fluctuations correlating with link acquisition, and referral traffic from suspicious sources all suggest link problems.
Essential Tools for Identifying Toxic Links
Professional SEO tools help identify problematic backlinks efficiently.
Google Search Console
Free essential tool showing links Google actually sees, manual action notifications appear here first, provides downloadable backlink reports, and shows most linked pages and anchor text.
Ahrefs Backlink Checker
Comprehensive backlink database and analysis, Domain Rating metrics for referring sites, toxic link identification features, anchor text distribution analysis, and referring domain quality assessment.
SEMrush Backlink Audit Tool
Automated toxicity score calculations, categorizes links by risk level, identifies patterns indicating problems, provides disavow file generation, and tracks backlink health over time.
Moz Link Explorer
Spam Score metric for referring domains, Domain Authority and Page Authority metrics, anchor text diversity analysis, link profile comparison features, and suspicious pattern detection.
Majestic SEO
Trust Flow and Citation Flow metrics, topical trust flow analysis, referring domain quality assessment, historical backlink data, and link context evaluation.
Step-by-Step Toxic Backlink Audit Process
Systematic auditing identifies all problematic links requiring action.
Step One: Export Complete Backlink Data
Download all backlinks from Google Search Console, export backlink reports from Ahrefs or SEMrush, combine data from multiple sources for completeness, and create master spreadsheet for analysis.
Step Two: Analyze Referring Domain Quality
Check Domain Authority or Domain Rating for each source:
- Flag domains with DA/DR below 20 for review
- Identify domains with high spam scores
- Note sites with no organic traffic
- Mark completely irrelevant industries
- Identify foreign language sites inappropriately
- Flag adult, gambling, or pharmaceutical sites
- Note hacked or malware-infected domains
Step Three: Evaluate Anchor Text Distribution
Review anchor text for over-optimization patterns, identify excessive exact-match keywords, flag unnatural commercial anchor text, note lack of branded or generic anchors, and calculate anchor text diversity ratio.
Step Four: Assess Link Context and Placement
Check whether links appear in main content or footers, verify links provide user value, identify site-wide footer or sidebar links, evaluate relevance of surrounding content, and note whether linking pages have substance.
Step Five: Identify Patterns and Clusters
Look for multiple links from related sites, detect link farm or PBN patterns, identify directory submission campaigns, spot negative SEO attack indicators, and flag sudden unnatural link spikes.
Understanding Spam Score and Domain Authority Metrics
Different SEO tools use various metrics to evaluate link quality. Understanding these scores helps you make informed decisions about which backlinks pose risks.
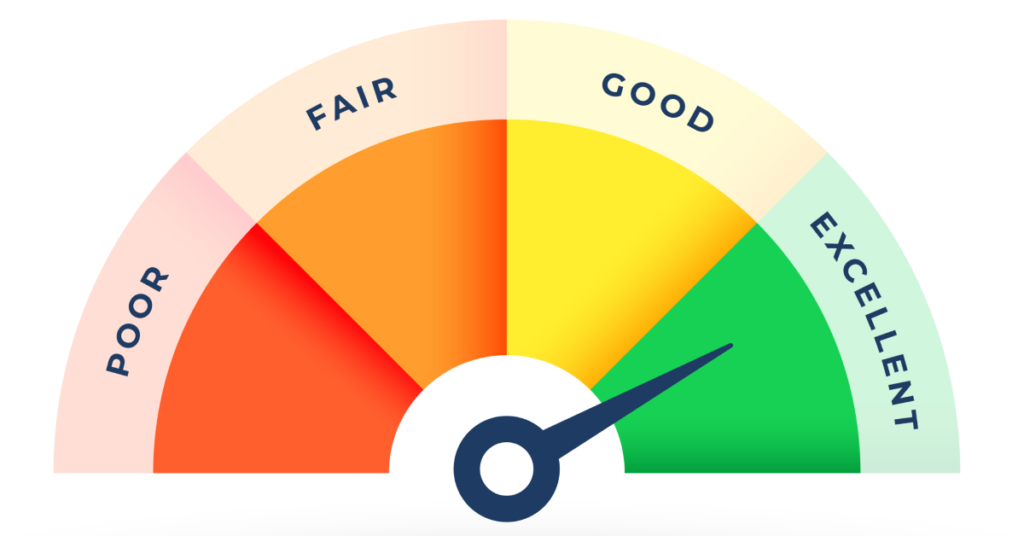
These metrics provide objective data for assessing referring domain quality, though no single metric tells the complete story.
Key Metrics Explained
Interpret quality metrics correctly for better decisions:
- Spam Score (Moz) measures 0-100% spam likelihood based on patterns
- Domain Authority predicts ranking ability on 1-100 scale
- Trust Flow shows link quality while Citation Flow shows quantity
- DA below 20 warrants review but isn’t automatically toxic
- Combine multiple metrics for accurate assessment
- Context matters more than any single number
- Manual review beats automated scores alone
Deciding Which Links to Remove or Disavow
Not every low-quality link requires action. Strategic prioritization focuses efforts effectively.
High-Priority Toxic Links
Links from known link schemes or PBNs require immediate action, backlinks from penalized sites, links with malware or security issues, obvious spam directory links, and links from adult or illegal content sites all demand removal.
Medium-Priority Concerns
Low Domain Authority sites in relevant niches may be acceptable, irrelevant but legitimate sites, overly commercial anchor text, and excessive footer or sidebar links all warrant evaluation.
Links to Leave Alone
Natural low-quality links that appear organic, occasional irrelevant mentions, user-generated content with nofollow tags, and natural branded anchor text even from low DA sites generally don’t require action.
When in Doubt
Google handles most low-quality links automatically, over-disavowing can remove good links accidentally, focus on obvious manipulation, and consult SEO professionals for borderline cases.
Manual Link Removal Process
Attempting manual removal before disavowing shows good faith to Google.
Finding Contact Information
Check site contact pages for email addresses, use WHOIS lookup for domain contacts, search LinkedIn for site owners, and try common email patterns like admin@domain.com.
Writing Removal Request Emails
Keep messages polite and professional, clearly identify the specific link, explain you didn’t request the link, ask for removal consideration, and provide exact URL details.
Email Template Example
Subject: Link Removal Request
Hi [Name],
I noticed a link to my site [yoursite.com] on your page [their-url]. I didn’t request this link and would appreciate its removal.
Link location: [specific URL and anchor text]
Thank you for your consideration.
Best regards, [Your Name]
Tracking Removal Efforts
Document all outreach attempts with dates, track responses and removals, follow up once after 7-10 days, and maintain records for Google reconsideration.
Negative SEO Attacks: Detection and Response
Competitors sometimes deliberately build toxic links to harm your rankings. Recognizing attacks early and responding quickly minimizes damage.

Negative SEO involves malicious link building, content scraping, or fake reviews designed to trigger penalties on your site.
Identifying Attack Patterns
Recognize negative SEO through these warning signs:
- Sudden spike in hundreds of toxic backlinks overnight
- Links from adult, gambling, or pharmaceutical sites
- Identical anchor text across many spam sites
- Links appearing on hacked or compromised domains
- Unnatural link velocity that you didn’t create
- Suspicious foreign language directory submissions
- Pattern suggests deliberate sabotage not organic growth
Response Strategy
Act quickly when attacks occur:
- Document all evidence with screenshots and dates
- Export complete backlink data immediately
- Submit disavow file without waiting for manual removal
- Report attack evidence to Google if severe
- Monitor daily during active attacks
- Focus on building quality links to dilute toxicity
- Consider professional help for severe cases
Using Google’s Disavow Tool Safely
The disavow tool tells Google to ignore specific backlinks when assessing your site.
When to Use the Disavow Tool
After manual removal attempts fail, when facing manual action for unnatural links, during negative SEO attack recovery, and for links from unreachable webmasters.
Creating Your Disavow File
Use plain text file format (.txt), list one URL or domain per line, use “domain:” prefix to disavow entire domains, add comments with “#” for documentation, and keep file organized and clean.
Disavow File Format
# Spam directory links
domain:example-spam-directory.com
# Specific page disavows
http://example.com/spam-page
# Hacked site links
domain:compromised-site.com
Submission Process
Access Disavow Tool in Google Search Console, select your property, upload your disavow file, review and confirm submission, and wait for Google to process (can take weeks).
Important Warnings
Disavowing good links can harm rankings, Google processes disavows slowly, effects aren’t immediate, overly aggressive disavowing causes problems, and incorrect format causes failures.
Monitoring Results After Link Cleanup
Track specific metrics to assess cleanup effectiveness.

Key Performance Indicators
Monitor organic traffic trends post-cleanup, track keyword ranking changes, watch for manual action removal, measure referring domain quality improvements, and assess overall domain authority changes.
Timeline Expectations
Manual action removal may take weeks after reconsideration, algorithmic recovery happens during updates, gradual improvement is more common than instant recovery, and patience is essential for results.
Ongoing Monitoring
Set up monthly backlink audits, monitor new suspicious links, track competitor backlink profiles, and maintain clean link profile proactively.
Preventing Future Toxic Backlinks
Proactive strategies minimize toxic link accumulation.
Quality Link Building Focus
Earn links through valuable content creation, build relationships with authoritative sites, focus on relevance over quantity, and avoid link schemes completely.
Regular Backlink Audits
Review new backlinks monthly, identify suspicious patterns early, remove problems before they accumulate, and maintain documentation of your link profile.
Negative SEO Protection
Monitor for sudden link spikes, set up alerts for unusual activity, respond quickly to attacks, and document evidence of negative SEO.
Your Toxic Backlink Management Plan
Protect your site’s rankings through systematic toxic link identification and removal. Start by conducting comprehensive backlink audits quarterly using Google Search Console and professional tools, identifying high-priority toxic links requiring immediate action, and documenting all findings systematically.
Remember that toxic backlink cleanup requires patience as Google processes changes slowly and recovery happens gradually over time. Focus on preventing future toxic links through white hat link building, maintain regular monitoring, and respond quickly to suspicious activity for long-term SEO health and sustainable rankings.