What Is the Difference Between On-Page and Off-Page SEO?
On-page SEO refers to optimization you control directly on your website, while off-page SEO involves activities outside your site that impact rankings. Both are essential for search success but work in fundamentally different ways.
Understanding the distinction helps you allocate resources effectively, prioritize optimization efforts, and build a complete SEO strategy that addresses both internal quality and external authority signals.
Understanding On-Page SEO Fundamentals
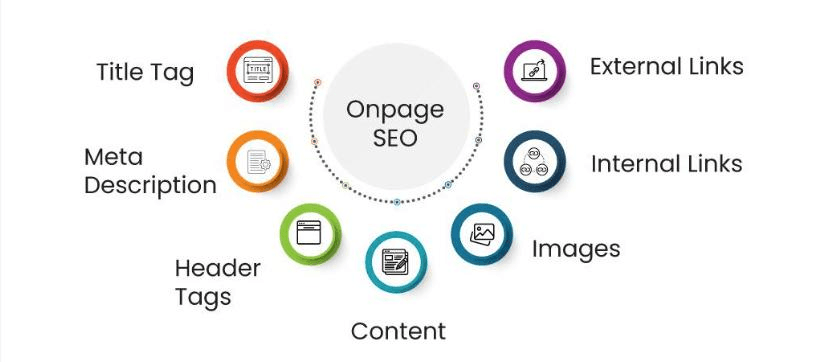
On-page SEO encompasses everything you do on your website to improve search rankings. This includes content optimization, technical improvements, site structure, and user experience enhancements.
The key advantage of on-page SEO is complete control. You decide what content to publish, how to optimize it, what technical improvements to make, and how to structure your site without needing permission or cooperation from others.
What On-Page SEO Includes
On-page optimization covers multiple elements you control directly:
- Content quality and relevance to search queries
- Title tags and meta descriptions for pages
- Header tag structure and keyword placement
- URL structure and permalink optimization
- Internal linking between your pages
- Image optimization and alt text
- Page speed and Core Web Vitals
- Mobile responsiveness and usability
- Schema markup and structured data
- Site architecture and navigation
Why On-Page SEO Matters
Strong on-page optimization helps search engines understand your content, makes pages more relevant for target keywords, improves user experience keeping visitors engaged, and provides the foundation all other SEO efforts build upon.
Control and Implementation Speed
On-page changes happen immediately when you implement them, require no external cooperation or approval, depend only on your time and resources, and deliver results relatively quickly once optimized.
Understanding Off-Page SEO Fundamentals
Off-page SEO involves activities outside your website that influence rankings. It primarily focuses on building authority, trust, and popularity through external signals.
The challenge of off-page SEO is limited control. You cannot force other sites to link to you, require time to build relationships, depend on others’ actions and decisions, and take longer to show results.
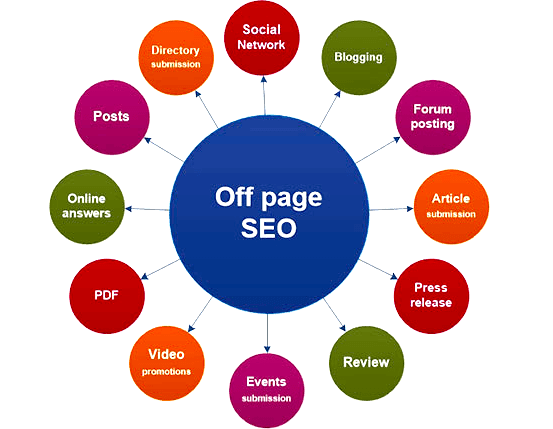
What Off-Page SEO Includes
Off-page optimization encompasses external ranking factors:
- Backlinks from other websites to yours
- Domain authority and trust metrics
- Brand mentions across the web
- Social media signals and engagement
- Online reviews and ratings
- Guest posting on other sites
- Influencer partnerships and outreach
- PR and media coverage
- Local citations and directories
- Community engagement and forums
Why Off-Page SEO Matters
External signals indicate popularity and authority, show search engines others trust your content, provide social proof of value and quality, and help you compete for competitive keywords requiring strong authority.
Building Takes Time
Off-page results accumulate gradually over time, require consistent effort and patience, depend on building genuine relationships, and cannot be rushed without risking penalties.
Key Differences in Control and Implementation
The most fundamental difference between on-page and off-page SEO is the level of control you have over optimization efforts.
On-page SEO gives you complete control to make immediate changes, while off-page SEO requires earning external signals you cannot directly control.
On-Page Control Advantages
You control every aspect of on-page optimization including what content you publish, how you structure pages, what technical improvements you make, and when changes go live without external dependencies.
Off-Page Control Limitations
Off-page success depends on others linking to your content, mentioning your brand, sharing your posts, and reviewing your business, all requiring persuasion rather than direct control.
Speed of Implementation
On-page changes take effect immediately once published, while off-page results build slowly as you earn backlinks, accumulate social proof, and establish authority over months or years.
Content Quality: The On-Page Foundation
Content forms the foundation of on-page SEO. Without quality content worth linking to, off-page efforts struggle because nobody wants to link to poor content.
Great content attracts natural backlinks, encourages social sharing, demonstrates expertise, and satisfies user intent completely.
Creating Link-Worthy Content
Content that naturally earns backlinks provides unique data or research, offers comprehensive guides, presents new perspectives, includes original examples, and solves problems better than competitors.
Content Optimization Elements
Optimize content by including target keywords naturally, structuring with clear headers, writing for your audience first, adding visual elements, ensuring accuracy and freshness, and making content scannable and engaging.
Link Building: The Off-Page Cornerstone
Backlinks remain the most important off-page ranking factor. Quality links from authoritative sites signal trust and relevance to search engines.
Not all links provide equal value, with links from relevant authoritative sites in your industry carrying more weight than random low-quality links.
Quality vs Quantity in Link Building
Focus on earning links from high-authority relevant sites, rather than accumulating many low-quality links, building diverse natural link profiles, and avoiding spammy link schemes.
Earning Natural Backlinks
Natural links come from creating outstanding content, building genuine relationships, providing value to others, becoming a trusted resource, and earning mentions through quality and expertise.
Strategic Link Building Methods
Effective link building includes guest posting on relevant sites, creating linkable assets, digital PR and outreach, broken link building, and resource page linking.
Technical SEO: Where Categories Overlap
Technical SEO spans both on-page and off-page categories. Site speed, mobile optimization, and structured data are on-page, while server location and CDN usage have off-page implications.
Technical optimization ensures search engines can crawl, understand, and index your content properly while providing good user experiences.
On-Page Technical Elements
Core on-page technical factors include page speed optimization, mobile responsiveness, Core Web Vitals scores, schema markup implementation, XML sitemap creation, and robots.txt configuration.
Off-Page Technical Considerations
Technical elements with off-page aspects include server location affecting speed globally, CDN implementation for faster international delivery, and DNS configuration impacting accessibility.
Authority Building Through Both Channels
Building authority requires combining strong on-page optimization with robust off-page signals. Neither alone suffices for competitive rankings.
On-page content demonstrates expertise, while off-page signals prove others recognize that expertise through links and mentions.
On-Page Authority Signals
Establish on-page authority through comprehensive content, demonstrating expertise, citing credible sources, maintaining accuracy, and regular content updates showing active expertise.
Off-Page Authority Signals
Build off-page authority via backlinks from authoritative sites, mentions in industry publications, recognition from influencers, positive reviews and ratings, and social proof through engagement.
Local SEO: Combining Both Strategies
Local SEO perfectly illustrates how on-page and off-page work together. Local businesses need both optimized website pages and external citations and reviews.

Local rankings depend on on-page location optimization, content about services, and off-page citations, reviews, and local backlinks.
On-Page Local Optimization
Optimize locally by including location keywords naturally, creating location-specific pages, adding local business schema, optimizing Google Business Profile, and providing clear NAP information.
Off-Page Local Signals
Build local authority through local directory citations, customer reviews on multiple platforms, local backlinks from community sites, local media mentions, and sponsorships or partnerships.
Time Investment and Resource Allocation
On-page and off-page SEO require different time investments and resource allocations for optimal results.
Understanding these differences helps you plan realistic timelines and allocate resources effectively between both areas.
On-Page Time Requirements
On-page work includes content creation time, technical implementation, site audits and fixes, and ongoing content updates, with results appearing relatively quickly once optimized.
Off-Page Time Investment
Off-page efforts require relationship building time, outreach and communication, content promotion, link building campaigns, and reputation management, with results accumulating gradually.
Balancing Resource Allocation
Effective strategies typically allocate 60-70 percent of resources to on-page optimization initially, then shift toward 50-50 balance as on-page foundation strengthens, with ongoing maintenance for both areas.
Which Matters More: On-Page or Off-Page?
The truth is both matter equally for complete SEO success. Focusing on only one severely limits potential rankings and traffic.
Strong on-page without off-page authority struggles against competitors with backlinks, while strong off-page cannot overcome poor on-page optimization and content.
Starting Priority: On-Page First
Begin with on-page optimization because you control it completely, it provides faster initial results, it creates foundation for off-page efforts, and quality content attracts natural links.
Long-Term Need: Both Together
Sustained success requires maintaining strong on-page optimization, building off-page authority consistently, monitoring both areas regularly, and adapting strategies as algorithms evolve.
Competitive Considerations
Competitive keywords require strength in both areas, while less competitive terms may rank with primarily on-page optimization, but authority still accelerates results.
Cost Comparison: Budgeting for On-Page vs Off-Page SEO
Understanding the cost differences between on-page and off-page SEO helps you allocate your budget effectively and set realistic expectations for investment and returns.
On-page optimization typically requires lower upfront costs but ongoing time investment, while off-page SEO often demands higher budgets for outreach, content promotion, and relationship building.
Breaking Down SEO Investment Costs
Plan your SEO budget by understanding these cost factors:
- On-page costs include content creation, technical audits and fixes, SEO tools and software subscriptions, and site speed optimization
- Off-page costs cover outreach and PR campaigns, guest posting opportunities, influencer partnerships, and link building services
- DIY approaches save money but require significant time investment and learning
- Agency services cost $500-$5000+ monthly depending on scope and competition
- ROI timelines differ with on-page showing results in 3-6 months and off-page requiring 6-12 months
- Start with on-page optimization for cost-effective foundation building
- Scale off-page investment as revenue and authority grow
Measuring Success in Each Area
On-page and off-page SEO require different metrics for measuring success and identifying improvement opportunities.
Understanding which metrics matter for each area helps you track progress accurately and identify where to focus optimization efforts.
On-Page Success Metrics
Track on-page performance through organic traffic growth, keyword ranking improvements, pages indexed successfully, Core Web Vitals scores, bounce rate reductions, and time on page increases.
Off-Page Success Metrics
Measure off-page success via backlink growth from quality sites, referring domain increases, domain authority improvements, brand mention frequency, social engagement rates, and referral traffic growth.
Common Misconceptions About Each Type
Several myths persist about on-page and off-page SEO that lead to misguided optimization efforts and wasted resources.
Understanding reality versus misconception helps you focus on strategies that actually work.
On-Page Misconceptions
Common myths include thinking keyword density matters more than relevance, believing more content always ranks better, assuming technical perfection alone drives rankings, and thinking on-page alone suffices for competitive terms.
Off-Page Misconceptions
Off-page myths include believing any backlink helps rankings, thinking quantity matters more than quality, assuming you can buy your way to authority, and believing social signals directly impact rankings.
Building Your Complete SEO Strategy
Successful SEO requires integrating both on-page and off-page efforts into a cohesive strategy that builds on strengths of each area.Start by establishing strong on-page foundations with quality content, proper technical optimization, clear site structure, and good user experience that gives searchers and search engines what they need.
Then build off-page authority through creating link-worthy content, developing genuine relationships, earning quality backlinks naturally, and building brand recognition consistently over time.
Remember that SEO success comes from excelling at both on-page and off-page optimization rather than choosing one over the other. The websites that rank best typically have strong optimization in both areas working together to demonstrate relevance, authority, and trustworthiness to search engines and users alike.